Nuclear Stress Tests
There are four types of cardiolite stress tests:
- Exercise cardiolite stress test
- Persantine cardiolite stress test
- Adenosine cardiolite stress test
- Dobutamine cardiolite stress test
 What is Cardiolite?
What is Cardiolite?
Cardiolite is a nuclear radioactive isotope termed Technetium Tc99m Sestamibi. Cardiolite is injected through an IV and it travels in the bloodstream and through the coronary arteries until it is picked up by the heart muscle cells. The areas of the heart that have an adequate blood supply pick up the tracer right away and more completely. Areas that do not have adequate blood supply pick up the tracer very slowly or not at all.
Cardiolite gives off a small amount of radiation that is detected with a nuclear scanning camera. A computer processes the information and produces the images of the radioactivity distributed in the heart.
If an area receives less blood than the rest of the heart (because of a blocked or narrowed artery), it will pick up a lower level of radioactivity and will show up as a lighter area, called a "defect."
Cardiolite is injected while you are at rest and while your heart is under stress. Rest and stress images are taken to allow doctors to compare how much blood flows through the heart muscle during stress and at rest.
The amount of radiation you will be exposed to is comparable to that from an X-ray or CAT (CT) scan. The half-life of Cardiolite is 6.02 hours. This means that half of the dose you are given will decay in 6.02 hours.
Generally, Cardiolite is cleared from your body in 24 hours by natural processes. You won't feel any different after you are injected with Cardiolite. Most patients experience no side effects. Occasionally patients have a metallic taste in their mouth.
What is a Cardiolite Stress Test and what does it show?
A Cardiolite Stress Test is a diagnostic nuclear imaging study that uses a radioactive tracer, called Cardiolite, to produce images of the heart muscle. When combined with stress either through exercise or use of a pharmacological agent, the Cardiolite scan helps determine if the heart muscle is getting the blood supply it needs.
As Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) progresses, the heart muscle may not receive enough blood when under stress (for example, when exercising). This often results in chest pain called angina pectoris. On the other hand, there may be no outward physical signs of the disease. If CAD is limiting blood flow to part of your heart, the stress test with Cardiolite may be useful in detecting the presence and significance of CAD.
A Cardiolite Stress Test consists of two parts, rest and stress:
- Cardiolite will be administered by injection through your IV while you are at rest, and a special camera will take pictures of your heart.
- Cardiolite will be administered to you one other time by an IV injection during the stress portion of the test, and additional pictures will be taken of your heart.
This allows the doctor to compare the amount of blood flowing through the heart muscle during stress and at rest.
How do I prepare for the test?
- Do not eat or drink for 4 hours prior to the test--this includes caffeine! The pictures of your heart are clearer when the stomach is not full. If you are diabetic or need to eat/drink with your medication, get special instructions from your doctor.
- Avoid any strenuous physical activity on the day of the test because you will need to exert yourself maximally if you are doing an exercise test.
- Bring busy material. You will have periods of waiting throughout the test so bring a book, newspaper, knitting, etc. to keep you busy.
- No smoking 4 hours prior to the test. Smoking may interfere with the test results.
- Wear a comfortable two-piece outfit and comfortable shoes. A hospital gown may be provided and men may be asked to take off their shirt. Slacks or shorts are preferred if you are exercising. You should wear comfortable footwear appropriate for brisk exercise if you are doing an exercise test.
- Do not wear oils or lotions before your test. Small sticky patches (electrodes) will need to stick to your chest.
- Do not take the following heart medications on the day of your test unless your physician tells you otherwise or if the medication is needed to treat chest discomfort:
- Isosorbide dinitrate (for example: Isordil, Sorbitrate)
- Isosorbide mononitrate (for example: Ismo)
- Nitroglycerin (for example: Deponit, Nitrostat)
- Your physician may also ask you to stop taking other heart medications on the day of your test. If you have any questions about your medications, ask your physician. NOTE: Do not discontinue any medication without first talking with your physician
What happens during the test?
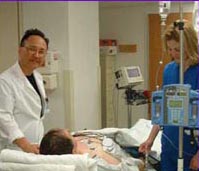
When you enter the stress testing room, the Cardiology Tech/Nurse will have you sign a consent form and he/she will make sure you understand the test. An IV will be started in a vein in your arm. The Nuclear Medicine Tech will put your first injection of Cardiolite through the IV. You will wait in the waiting room for at least 45 minutes to let the Cardiolite circulate to your heart.
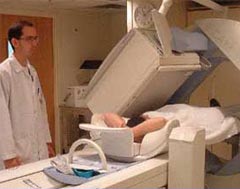
Once your waiting period is over, the Nuclear Medicine Tech will put you under the camera for about 15 minutes. You will lay on your back on a table with your hand behind your head. It is important for you to remain very still while the images are being taken. The camera will move about you but never come in contact with you during the scan.
Following the completion of the scan, you will be escorted to a stress testing room. The Cardio Tech/Nurse will have you lay on a stretcher while he/she hooks you up to equipment. A bag of normal saline will be attached to your IV. The chest will be abraded with alcohol and a cloth. If you have a hairy chest, patches will be shaven. Ten electrode patches are placed on your chest and torso. Wires will be attached to the electrodes in order to monitor your heart rate and EKG. A resting EKG and blood pressure are recorded. Once the Cardiologist arrives in the room, your test will begin.
Persantine Cardiolite Stress Test
For patients who are unable to exercise adequately on the treadmill, the drug Persantine may be given to produce an effect on the heart similar to exercise. During the test, you will be lying on the stretcher. A line of normal saline will be connected to your IV. The drug Persantine will be infused through your IV. The Persantine dosage you will be given is based on your body weight. Persantine is a vasodilator so you may feel warm, flushed, experience chest pressure, headache, dizziness, nausea or shortness of breath. These symptoms are perfectly normal, but make sure to let the Cardiologist know how you feel. The Persantine is infused over 4 minutes. Two minutes will lapse. Then you will be given another injection of Cardiolite. After the Cardiolite injection, you will be given the drug Aminophylline if you are experiencing any symptoms from the Persantine. In some cases, the Cardiologist will have you perform hand squeezing exercises to help get more accurate test results.
What is Persantine?
 Persantine is a coronary vasodilator that is used as a diagnostic agent in nuclear stress testing. Persantine works by increasing the blood vessel circumference of the coronary arteries (arteries that feed the heart) in order to increase blood flow to the heart. Persantine causes a 20% increase in heart rate and a mild but significant decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Persantine is metabolized in the liver. The amount of Persantine you will be given is based on your body weight.
Persantine is a coronary vasodilator that is used as a diagnostic agent in nuclear stress testing. Persantine works by increasing the blood vessel circumference of the coronary arteries (arteries that feed the heart) in order to increase blood flow to the heart. Persantine causes a 20% increase in heart rate and a mild but significant decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Persantine is metabolized in the liver. The amount of Persantine you will be given is based on your body weight.
Side effects include: chest pain/pressure, dizziness, headache, nausea, dizziness, shortness of breath, or a warm and flushed feeling. Some patients experience a burning or stinging sensation at their IV site because Persantine is more acidic than your blood. Persantine is contraindicated in patients who have a hypersensitivity to this drug. Persantine can also cause bronchospasm so your doctor may order a different test for you if you have a lung condition that will be exacerbated by using Persantine.
If you do develop side effects to Persantine, the Cardiologist will use the antidote Aminophylline to reverse your side effects.
Adenosine Cardiolite Stress Test
An adenosine cardiolite stress test is identical to a Persantine cardiolite stress test, using a different dilating medication, Adenosine.
What is Adenosine?
Adenosine is an antiarrhythmic agent that is used as a diagnotic agent in nuclear stress testing. Adenosine acts as a vasodilator and its actions are similar to that of Persantine. It also increases the blood vessel circumference of the coronary arteries (arteries that feed the heart) in order to increase blood flow to the heart. Adenosine has a short half-life (less than 10 seconds). This means, any side effects you may experience will be generally predictable, short lives, and easily tolerated. Side effects include: chest pressure, dizziness, shortness of breath, flushing, headache, lightheadedness, nausea, or numbness. Adenosine is contraindicated in patients who have a hypersensitivity to this drug and in patients who have a known or suspected bronchospastic or bronchoconstrictive lung disease (e.g., asthma).
If you do develop side effects to Adenosine that do not disappear quickly, the Cardiologist will use the antidote Aminophylline to reverse your side effects.
Dobutamine Cardiolite Stress Test
 For patients who are unable to exercise adequately on the treadmill, the drug Dobutamine may be given to produce an effect on the heart similar to exercise. During the test, you will be lying on the stretcher. A line of normal saline will be connected to your IV. The drug Dobutamine will be infused through your IV. The Dobutamine dosage you will be given is based on your body weight. Dobutamine is infused slowly through your IV, and the dose is increased every 3 minute. The Dobutamine infusion is turned off after it is infused for about 12 minutes. The Dobutamine may be turned off early if:
For patients who are unable to exercise adequately on the treadmill, the drug Dobutamine may be given to produce an effect on the heart similar to exercise. During the test, you will be lying on the stretcher. A line of normal saline will be connected to your IV. The drug Dobutamine will be infused through your IV. The Dobutamine dosage you will be given is based on your body weight. Dobutamine is infused slowly through your IV, and the dose is increased every 3 minute. The Dobutamine infusion is turned off after it is infused for about 12 minutes. The Dobutamine may be turned off early if:
- You exceed a "target" heart rate based on your age
- The Cardiologist or Cardio Tech/Nurse detects abnormal changes on your EKG
- You experience significant symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, chest tightness, dizziness, etc. that do not permit you to exercise any longer.
- Your blood pressure goes up too high
The dobutamine is infused longer than the 12 minutes if your heart rate has not reached the predicted "target" heart rate. Sometimes the Cardiologist will have the Nurse give you a drug called Atropine through your IV if your heart rate has not sufficiently increased. You will be given one more injection of Cardiolite once your heart rate is at or has exceeded your "target" heart rate. Sometimes the Cardiologist will have the Nurse give you a drug called Lopressor through your IV if your heart rate is taking a long time to decrease.
Surgeries
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
- Bypass Surgery
- Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA)
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG)
- Transmyocardial Revascularization (TMR)
- Valve Repair Surgery
- Valve Replacement Surgery
Procedures
- Ablation
- Angiojet Thrombectomy
- Aortagram
- Atherectomy
- Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (AICD or ICD)
- Coil Embolization
- Computed Axial Tomography (CAT or CT)/Ultrafact Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
- Coronary Balloon Angioplasty & Stenting
- Coronary Catheterization
- Dobutamine Stress Echo
- Echocardiography (ECHO)
- Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG)
- Electrophysiology Study (EPS)
- Event Recorder
- Holter Monitoring
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Umbrella Placement
- Intraaortic Balloon Pump
- Intracardiac Ultrasound (ICE)
- Intravascular Ultrasound (ICE)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)/ Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
- Medicated Stents
- Nuclear Stress Tests
- Pacemakers
- Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA)
- Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA)
- Peripheral Stents
- Peripheral Vascular Angiography
- Radiation Brachytherapy
- Septal Closures
- Signal Averaged Electrocardiogram (SAECG)
- Stents
- Stress Echocardiogram
- Stress Test
- Thrombolytic Treatment
- Tilt Table
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
- Valvuloplasty
